OEE Evaluation
supOS boasts on the application of UNS (Unified Namespace), and here we use an example to show how supOS evaluates equipment performance based on OEE calculated from different types of data.
Example Description
We will use supOS to connect and format equipment running time, product quantity and product quality data, adopt AI model analyze equipment performance based on the OEE (Overall Equipment Effectiveness) metrics and send the result back to supOS for subsequent display.
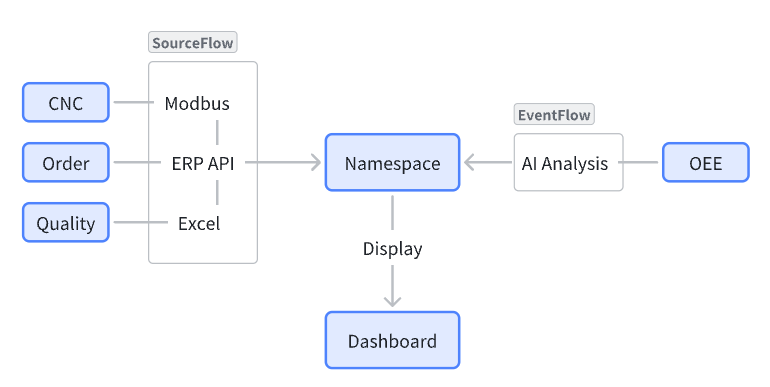
Data Source
- CNC running time data connected and monitored by PLC through Modbus
- Order information from ERP system transmitted by RestAPI
- Product quality log recorded on an Excel table
In this example, we will use simulated data to demonstrate the process.
Data Integration
Building Data Models
Build data models to store data in supOS, and at the same time, MQTT topics with identical name will be created in the embedded MQTT broker.
- Log in to supOS, and then click Namespace under UNS.
- Click
 to add a path (namespace) named Equipment.
to add a path (namespace) named Equipment.

- Click
 to add a topic (data tag) named CNC under the Equipment, and add attributes to store the actual running time and planned running time data of the equipment.
to add a topic (data tag) named CNC under the Equipment, and add attributes to store the actual running time and planned running time data of the equipment.

- Click Next, and select Enable History to store history data.

- Apply the same operation to add relational model Order/OrderInfo, Quality/OrderQualityLog, Quality/QualityAnalysis.
| Model | Attribute | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Order/OrderInfo | sum/double, time/double | Indicates the quantity of products and the time consumption for making a single product. |
| Quality/OrderQualityLog | Sum/double, Good/double, Rate/double. | Indicates the overall quantity of products, quantity of certified products and certified rate. |
| Quality/QualityAnalysis | performance/string | Indicates the overall equipment performance. |

Adding Data Sources
When finishing building data models, NodeRed data flows with mock data will be generated in Source Flow. We need to change the data sources of the flows to get real data.
Getting Equipment Running Time
- Click Source Flow under UNS, and then click Equipment/CNC.

- Change the data source to
Modbus, add the Modbus server and enter corresponding configurations.
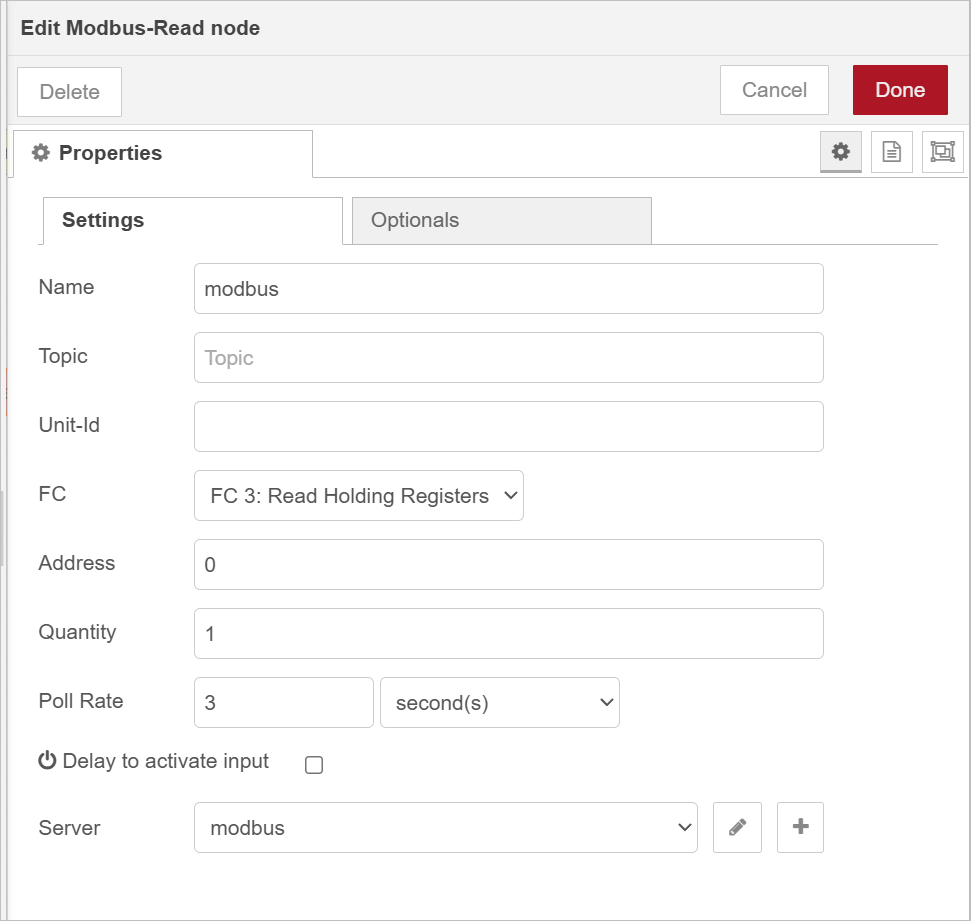
Make sure the output data of Modbus read node is an object and matches that in UNS. Otherwise, use a function node to do data conversion.
-
Add
Debugnodes, and then click theModebusnode to trigger the flow. -
Check whether the data is transmitted to Namespace.

Getting Order Information
- On the Sourc Flow page, click Order/OrderInfo.
- Change the data source to RestAPI, and enter the API information.
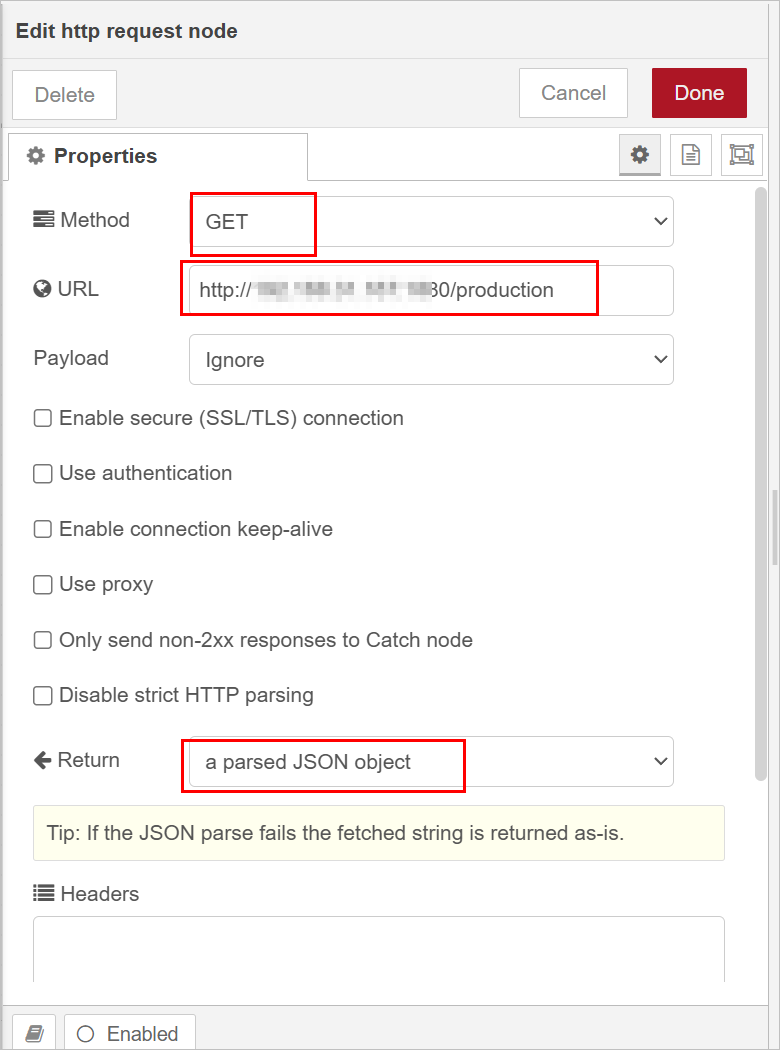
Use a function node for conversion if the API does not transmit OBJECT type of data with keys matching the keys in UNS models.
-
Add
Debugnodes, and then trigger the flow. -
Check whether the data is transmitted to Namespace.

Getting Product Quality
-
On the Source Flow page, click Quality/OrderQualityLog.
-
Change the data source to excel file.
- Save the Excel file to the server where the NodeRed is deployed.
- Use a
read filenode to access the Excel table.

- Extract data from the Excel table.
You need to install node-red-contrib-spreadsheet-in node to extract data.
- Add a function node, wirte a script to format the transmitted data to JSON object.
- Add
Debugnodes, and then trigger the flow. - Check whether the data is transmitted to Namespace.

Analyzing Data
Integrates all data sources and analyze them with AI models, eventually sends the results back to Namespace.
- Click Event Flow under UNS, and then click New Event Flow at the upper-right corner to add an event flow.
- Click the flow, and then drag 3
mqtt innodes to the canvas. - Double-click the nodes, add the embedded broker named emqx, and then subscribe to the topic Equipment/CNC, Order/OrderInfo and Quality/OrderQualityLog from Namespace.

- Install
factory-agent-statesandfactory-agent-deepseeknodes, and connect all 3 data sources withfactory-agent-statesnode to integrate all data.
These nodes are customized and uploaded to NodeRed. For details, see factory-agent-states and factory-agent-deepseek.
- Set the delay time to more than 10 seconds, and write the prompt for using Deepseek.
- Add a function node to write necessary parameters for the
factory-agent-statesnode to output all cached topic messages.
factory-agent-states caches data transmitted to it after receiving all of them. It is better to give a reasonable delay time to receive all data before operation.


- Connect another function node to
factory-agent-statesto calculate OEE and better the prompt.

- Connect the
factory-agent-deepseeknode to the function, enter the Deepseek key and select deepseek-reasoner model.

- Add another funtion node to extract result information from the Deepseek response.
supOS Namespace has a limit for receiving data volume (256 bytes). We recommend you to split the response.

- Drag an
mqtt outnode, and subscribe to the topic Quality/QualityAnalysis.

- Trigger the flow in order and go to Namespace to check the result.
- Trigger all 3 data source flows under Source Flow.
- Trigger the flow to send parameter to
factory-agent-states.


Data Display on Dashboard
supOS combines Grafana to complete the flow of data collection, analysis and display.
- Add a function node in Event Flow to get the AI analysis result.

- Add another data model under Namespace to store the result.
- Go to System > Dashboards, and then add a new dashboard.
- Click the dashboard, and then click Add visualization.
- Select a data source.
- Time series data (Equipment/CNC) is stored in TDEngine.
- Relational data (Order/OrderInfo, Quality/OrderQualityLog) is stored in Postgresql.
- All data in Namespace is transmitted through MQTT broker.
If there is no MQTT, you can click Configure a new data source, search for it and configure it.


- Design the dashboard.

- Save the dashaboard and then click Preview.
